Our Announcements
Sorry, but you are looking for something that isn't here.
Posted by admin in PAKISTANI POETRY on September 28th, 2013
زندگی
 اک معمہ ہے پر اسرار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
اک معمہ ہے پر اسرار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
زندگی جیسے کہ اک بار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
بات بنتی ہی نہیں راز کہ کھلتا ہی نہیں
نسل آدم ہی سزاوار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
وہ تو اچھا ہے جو آ یا نہیں اس دنیا میں
او ر جو آیا ہے وہ لاچار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
مر کہ ہی جانا ہے جنت میں جنھیں جانا ہے
موت کیوں راہ کی د یوا ر ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
درد دل بانٹنے نکلو تو یہی لگتا ہے
جیسے ہر شخص ہی بےزار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
درس دیتے ہیں محبت کا اگر لوگ تو پھر
ہر کوئی د ر پۓ آ ز ا ر ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
کوئی ایسا ہے فرشتوں کو بھی جو مات کرے
دوسرا سخت گنہگار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
ہر خو شی پر رہے بیتاب یہ گرنے کے لیے
غم کہ لٹکی ہوی تلوار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
رات کیوں دن کے تعا قب میں لگی رہتی ہے
پھول کے ساتھ لگا خا ر ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
مر ے اس پیا ر کے بدلے میں جو چھم چھم برسے
ترے طعنو ں کی جو بوچھاڑ ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
حسن کو چا ھیۓ وہ بھی تو کبھی پہل کرے
صرف عاشق ہی طلبگار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
جس کو کہتی ہیں بڑ ے فخر سے قومیں غیرت
ہم نے بیچی سر بازار ہے ایسا کیوں ہے
Posted by admin in Pakistan Army's Biggest Enemy Nawaz Sharif, Pakistan Security, Pakistan Security and Defence: Enemy & Threats (Internal & External) on September 28th, 2013
A COMMENT ON A RETIRED SENIOR OFFICER OF PAKISTAN
NAME WITH-HELD
Dear Sir ………….
I read with interest the assessment regarding the next chief. Some of the contenders like Tariq and Haroon have been my students during various stages of their career and one knows them well as also their reputation in the army.
Interestingly the largest analysis you did was on Tariq which itself says something.
As I told you earlier he is the best thing that could happen to the Army…… amongst the young officers he is called ‘Bull dozer’…….
Haroon who was my student on the war course is known as ‘Apa’ (ha ha)………. Not a good nickname for a potential army chief.
I also know all the ‘advisors’ that you have identified (again some I have served with …Qayyum……… and others who have been my students ….. Qadir and Javed………) and unfortunately I do not grade any of them with an intellect or ability that would guide them towards making an unbiased recommendation.
God help us all and God help Pakistan.
Posted by admin in Pakistan Army on September 28th, 2013

‘We cannot afford to confine Army appointments to persons who have excited no hostile comment in their careers …. This is a time to try men of force and vision and not to be exclusively confined to those who are judged thoroughly safe by conventional standards’. Prime Minister Winston Churchill to Sir John Dill, Chief of Imperial General Staff, 1940
Pakistan army is a major player on national scene therefore change of command generates unusual interest both in the country as well as the outside world. Two top positions are Chairman Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee (CJCSC) and Chief of Army Staff (COAS). Theoretically, CJCSC is senior but practically this position is ceremonial and real power holder is COAS. Main reason is that COAS controls the army with promotions and postings. CJCSC can be selected from any of the three services but this post has been used to placate or reward some senior army officers, therefore for the last seventeen years this post is held by a senior army officer. Last time when an air force or naval officer held the position of CJCSC was in 1997. Current CJCSC General Khalid Shamim Wayen will be retiring on October 06, 2013 and COAS General Ashfaq Pervez Kayani on November 28, 2013.
Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif will be deciding about next appointment of COAS. His two close civilian advisors are his younger brother and chief minister of Punjab Shahbaz Sharif and interior minister Chaudhry Nisar Ali Khan. He consults with these two about all important issues. On military matters, he gets limited input from few retired officers. These include retired Lieutenant General Khwaja Ziauddin, retired Lieutenant General Abdul Qadir Baloch, retired Lieutenant General Abdul Qayyum and Brigadier Javed Malik (for brief profile of these officers see Appendix: I below). The role of these officers is very limited regarding advice about selection of new COAS. Their relationship is that of an acquaintance and not close confidant. In my view, advice from his close civilian associates will carry more weight than any army officer. In general, there is no culture of reading serious material or informed debate. Civilian leadership including Nawaz Sharif is not known for reading or soliciting advice from informed individuals about critical issues. I don’t think that country’s top ten decision makers have read a complete book in the last one year. A small group around Nawaz Sharif tries to whisper in King’s ears and general style is more close to a sixteenth century princely state with sycophancy and intrigues of Byzantine proportions.
In normal process, COAS is usually selected from top four or five senior officers. Most of these officers are average, equal in qualifications and rotated through normal command, staff and instructional appointments at senior ranks. My own assessment is that seventy percent are average officers and not very different from officers found in other armies. Twenty percent are below average and able to pass through the promotion labyrinth due to special circumstances. Ten percent are first rate and any army could be proud to have them among its ranks. Opinions of their colleagues, superiors, juniors, friends and family members are highly subjective in nature.
Selection of army chief is essentially a political decision and in addition to qualifications, ability of the individual to work with government on important issues is considered. COAS tenure is three years and in case of Pakistan many army chiefs got extensions to the detriment of the institution. I’ll review the tenure of General Kayani and his decision making process, challenges of the next three years for new chief and brief overview of career and my opinion about each potential candidate.
General Ashfaq Pervez Kayani was appointed by outgoing COAS General Pervez Mussharraf when he was forced to give up his post after nine years. Mussharraf’s choice was between Kayani and Lieutenant General (later General) Tariq Majeed. Majeed was more assertive compared to Kayani who played more safely keeping his thoughts to himself. Mussharraf may have felt Kayani will work with him better as Musharraf was to remain President after shedding his uniform. Kayani became close to Musharraf when he was given the charge of investigating assassination attempts on Musharraf’s life. Kayani was then commanding Rawalpindi based X Corps and his diligent work brought him close to Mussharraf and paved the way for his future rise. He was appointed Director General of Inter Services Intelligence (DGISI) where he served for three years. In November 2007, he was appointed COAS.
Kayani had the most difficult task for the first few months facing challenges on many fronts. First and foremost, he gradually got control of the army easing out Mussharraf’s appointees and bringing his own team of confidants. His second task was to move army away from civilian affairs and hands off policy for 2008 elections. He managed a delicate balance of avoiding direct confrontation with Mussharraf while at the same time following his own independent course. He didn’t bail out Mussharraf when later got into serious troubles and threatened with impeachment. However, Kayani worked behind the scene to make sure that Mussharraf was not humiliated. A back ground deal managed a safe exit for Mussharraf in 2008 for a comfortable exile in London and Dubai (he recently came back despite repeated advice from army’s brass to stay put abroad and now facing court cases).
Kayani’s second task was to reorient army to new challenges. When Kayani took charge of the army, things were in disarray and morale was quite low as militants had taken the fight to the military and army suffered many reverses. Gradually, counterinsurgency methods were introduced in all training institutions and things improved. Two decisions of keeping military away from direct interference and reorientation of army are credit to Kayani. His major weakness is very slow decision making process. Many of the decisions which he finally took were forced from pressure at various levels. Pressure from junior officers deployed in forward areas forced Kayani to finally decide about some military operations against militants. In addition, push from inner circle of Corps Commanders forced some other decisions.
Some promotions and appointments to key positions were disastrous and resulted in lot of murmuring in the army. Lieutenant General Ahmad Shuja Pasha is an infantry officer with very good reputation. He is a straight forward chap who could be very good commander of an infantry division but completely unsuited for the job of top spy. His personality and temperament was not for the job of DGISI and the fall out was quite negative. Kayani had a very favorable opinion about Pasha but never vigorously challenged his advice or actions. Kayani and army got entangled in some controversies due to actions of Pasha. Army had no love lost for Pakistan’s ambassador to Washington Mr. Hussain Haqqani. Pasha jumped on what was later known as Memo Gate scandal. Pakistan army accused that Mr. Hussain Haqqani asked for U.S. help to thwart army’s attempt to subvert civilian leadership at the behest of then Pakistan’s President Asif Ali Zardari in the aftermath of U.S. raid that killed Osama Bin Ladin in Pakistan. In another case, during visit to Washington, Kayani handed a report to White House titled Pakistani Perspective with lot of half baked theories currently in vogue at ISI that severely damaged Kayani’s own standing. Kayani never challenged kidnap, torture, kill and dump policy of army’s intelligence operatives in Baluchistan. Thanks to this policy, all segments of Baluch society are now thoroughly alienated. The problem that started as disagreement on monetary benefits to few Baluch tribal leaders is now transformed into a nationalist movement. ISI officers whose own offices were bombed by militants were promoted and in one case a two star under whose charge dozens of soldiers deserted was awarded with a third star. In peacetime, these things may not count much but during the time of war such decisions eat the organization from inside and should be avoided at all costs.
Kayani’s attempts to create circumstances for his own extension of service severely undermined his credibility inside the army. He gave extensions to some senior officers creating an impression that somehow extension is a norm rather than exception. When his unprecedented three year extension was announced, it caused lot of resentment. In the aftermath of the U.S. raid that killed Osama Bin Ladin, Kayani’s stock hit the lowest point. Pasha and Kayani duo successfully diverted the attention when Pasha cursed Americans in a briefing to parliament with thunderous applaud from the audience. They also turned their guns on President Zardari and Pakistan’s ambassador to Washington Hussain Haqqani and vetted their anger by hanging poor Dr. Shakil Afridi (it was alleged that he tried to get blood samples from the residents of Bin Ladin compound for CIA) by his thumbs. Government’s own credibility was so low due to utter incompetence and corruption that in comparison to civilian leaders, Kayani looked like an angel and he recovered quite quickly from these set backs.
There are already rumors that Kayani may be given a one year extension or sent as an ambassador. Both options are bad and should be avoided. Previous three year extension had much more negative impact on all areas and I can not see anything positive and fruit of another extension will also be bitter. Senior army and police officers involved in operations against militants have been targeted and many have been killed. In some cases, army sent officers involved in operations as ambassadors and some privately departed for Dubai after retirement. This has severely undermined army’s reputation on the street. Police officers now make fun of their army colleagues privately. Sending Kayani as ambassador immediately after retirement will strengthen this impression as every one will rightly conclude that this is being done due to threat to his life. Army should be able to provide security to its own former chief in his own country. Many mid-level officers are concerned about their security and the least Kayani can do is to stay put for at least a year or two in the country. Once things settled down and people forget then if he wants, he can go into the safety of a comfortable diplomatic sojourn.
COAS is just one player on the scene and country is facing challenges on many fronts. The challenges for new army chief for the next three years include;
– Coordination with civilian leadership on three crucial issues of containing militancy, reorienting policy towards Afghanistan and continue to keep eastern border with India quite.
– Leading armed forces in a state of war providing clear mindset, strategic roadmap and operational guidance. He will be responsible for promoting next line of officers and this is the most important task.
– Taking lead, immediately halting kill and dump policy in Baluchistan and start reconciliation with Baluch nationalists.
Five Senior Most Lieutenant Generals in Order of Seniority are:
Lieutenant General Haroon Aslam is from 52nd PMA course and commissioned in October 1975. He is currently Chief of Logistics Staff (CLS) after commanding XXXI Corps based in Bahawalpur. He spent good part of his career in Baluchistan where he first served as Chief of Staff (COS) of Southern command and later commanded an infantry division based in Quetta. He commanded operations against militants in Swat when he was General Officer commanding (GOC) of Special Services Group (SSG). He is an average officer with some experience of fight against militancy. However, in my view, if selected he will not be better than Kayani. It is possible that being senior most, he is appointed CJCSC as Nawaz Sharif in his manifesto stated that he will adhere to the principle of seniority.
Lieutenant General Rashad Mahmud is also from 52nd PMA course and commissioned in October 1975. He is currently serving as Chief of Staff (CGS) after a stint as Corps Commander of IV Corps based in Lahore. He is Kayani’s preference as his successor. He is also an average officer. He was DAPS to army chief General Mirza Aslam Beg at the rank of Major under then Brigadier Khwaja Ziauddin who was Personal Secretary to Chief – PS (C). Later, at the rank of Brigadier, he served as Military Secretary (MS) to President Rafiq Tarar. His general career pattern and service in staff positions suggests that if selected he will be more formal with no inclination for any new ideas. In my view, if selected, he will be no better than Kayani. Only positive thing is that he had served as Counter Terrorism (CT) Director at ISI. Some see this as an asset while for others this is a liability in view of relationship of ISI with some militant groups. In my view, he would have been good enough for a peacetime army but not a wartime army. He is a better candidate for CJCSC position rather than COAS.
Lieutenant General Raheel Sharif is from 54th PMA course and commissioned in October 1976. He is currently serving as Inspector General of Training & Evaluation (IGT&E) after commanding XXX Corps based in Gujranwala. He is from a military family and his father, two brothers and a brother-in-law served in the army. His brother Major Shabbir Sharif is one of the most decorated soldiers of Pakistan army who was killed in action in 1971 war. Life of sons or brothers of heroes is a difficult one as expectations are very high. Shabbir was General Pervez Mussharraf’s course mate. Shabbir was everything that Mussharraf wanted to be. When Mussharraf became COAS, he was instrumental in grooming Raheel for higher ranks. In fact, Raheel was selected as personal secretary to army chief but Mussharraf later changed his mind and instead sent him to prestigious Royal College of Defence Studies (RCDS) course in London. Raheel was COS of XXX Gujranwala Corps under Lieutenant General Abdul Qadir Baloch. In major reshuffle in the aftermath of September 11, 2001, Qadir was sent to Quetta based XII Corps and he took Raheel with him as COS. Mussharraf promoted him to major general rank and gave him prized postings as GOC of Lahore based 11th Infantry Division and Commandant of Military Academy at Kakul. Raheel is a gentleman but almost all agree that for a peacetime army, it would make no difference but probably he is not suited to lead army engaged in a war. I think Raheel himself knows it but Lieutenant General ® Abdul Qadir may whisper some good words about him in Sharif’s ears.
Lieutenant General Tariq Khan is from 55th PMA course and commissioned in April 1977. He was best cadet winning coveted Sword of Honor. He is currently commanding Mangla based I strike corps. He is a Pushtun cavalry officer and his father was also a cavalry officer. Tariq is from an aristocratic family and from the breed that didn’t join army for a secure job. After a brief stint of commanding an armored division, he first commanded infantry division in Waziristan and later as Inspector General Frontier Corps (IGFC) transformed a shattered FC. In my view, he is the only officer among the contenders who has the qualifications for leading the army in the coming turbulent three years. He is head and shoulders above his peers. His straight forward and professional approach is sometimes construed as ‘hard headed’. He has earned the nick name of ‘bulldozer’ for nothing. I don’t know any other officer who has so much red ink in his file and that he made it so far is only due to his professional competence which even his detractors admit. He was one of only two major generals highly regarded by Kayani for their professional competence (the other being Ahmad Shuja Pasha).
Some label him as ‘rash’ and ‘pro-American’. I can understand why some label him as ‘rash’. Tariq is frank to the point of bluntness and not hesitant to speak his mind which invariably results in some friction. He is a hard task master and in operations, he took decisions and many times clashed with his seniors while as Corps Commander he is training his formation hard. In time of war, I’ll pick a so-called ‘rash’ officer anytime compared to someone who was busy opening restaurants and bakeries in cantonment or planning for expansion of defense housing schemes. Some consider Tariq as ‘pro-American’ and I think this is due to his views about militancy. He was one of the few senior officers who comprehended right from the beginning that menace of militancy is an existential threat to Pakistan. It took several years for General Head Quarters (GHQ) to get this point. He was at the forefront of many operations against militants. He commanded an infantry division in South Waziristan and later as IGFC, he transformed a demoralized and broken formation into a credible fighting force. U.S. provided funds for FC modernization and a handful of U.S. Special Forces soldiers provided limited training in some special skills. This very limited interaction is exaggerated due to lack of information. In the last ten years, in addition to FC, Washington also supported intelligence agencies in technical matters as well as Pakistan’s Special Forces. In view of deteriorating relations in the last two years, most of these relations have been terminated.
In the last ten years, there has been increased military to military interaction between United States and Pakistan and a number of officers at different ranks visit U.S. for training and attend various seminars and conferences designed for senior officers. Tariq has not done any course in United States nor attended any conference or seminar designed for senior officers. His only American connection is stint as liaison officer at CENTCOM headquarters in Tampa at the rank of Brigadier (since 2001, a small team of Pakistani officers commanded by a Brigadier rank officer serve as liaison with CENTCOM). In fact, in 2008, Americans had serious misgivings about his approach in Bajuar. American military had embraced the counterinsurgency by that time and with the zeal of a new convert, they viewed Tariq’s approach as faulty and viewed it as scorched earth policy. In Bajuar, years of neglect had resulted in hardened militant positions especially tunnels that needed heavy fire power. Later, some Americans were content that at lest some Pakistani officers were doing that was needed to clear the badlands. It was confluence of interests and not any special affinity of Tariq for Americans or vice versa. In fact a professional and proud officer will work on common interests but will assert himself when needed. When Tariq was IGFC, cross border fire resulted in death of two FC soldiers. He put his foot down and pushed GHQ for a tough line. Washington was forced to agree to a joint inquiry at Bagram and admit mistake. General David Petraeus was forced to publicly apologize to Pakistan. I can not recall when the last time Washington agreed to a joint inquiry during war and offered a public apology.
Tariq is the kind of officer to lead army in war time. If selected, he will be a significant improvement from Kayani. However, one needs to be realistic that even selected, he does not have the key to success. He can be an important lever to contain and push back militancy but a true national effort will be needed to bring country back on tracks. Taking territory from militants is a vital first step but in such kind of war you can not shoot your way to victory. At some point, de-radicalization and re-integration especially of foot soldiers will be an important part of the strategy and there is concern that an officer who has spent so much time in fighting may ignore this important aspect.
Lieutenant General Zaheer ul Islam is also from 55th PMA course and commissioned in April 1977. He is currently Director General (DG) of Inter Services Intelligence (ISI). He had an earlier stint as Director at ISI prior to his elevation to lieutenant general rank and posting as Corps Commander of Karachi based V Corps. He is from a military family and belongs to the traditional military recruiting area of Salt Ranges near Rawalpindi. He is an average officer who has done usual command and staff stints but nothing exceptional in his professional career. He is not likely in the race and even if selected, he will be about same as Kayani as far decision making is concerned.
No army including Pakistan army has any Rommel or Guderian among its ranks. There is no ‘knight on white horse’ that will be the savior. It is a hard road ahead for Pakistan and collective effort will be needed to steer the ship to calmer waters. There will be difference of opinion but civil and military leaders should remember the basic fact that they are on the same team. Criteria of selection of a senior officer for a peacetime army and an army at war should be different. Simple fact is that Pakistan is at war and therefore officers with sound judgment, initiative, innovative ideas and very high professional standards should be considered for senior positions rather than docile and presumably ‘loyal’ who will not likely stir any discussion or debate at the decision making table.
|
Appendix: I
Lieutenant General ® Khwaja Ziauddin: A mild mannered gentleman and average officer. There was no history of any problem between Mussharraf and Ziauddin. Ziauddin was from Engineers Corps and their paths have not crossed during their professional career. In September 1998, when Mussharraf was appointed COAS, he immediately settled down in Armor Mess (General Jahangir Karamat was still in Army House) and started shuffling the senior brass. Ziauddin then serving as Adjutant General (AG) was with him. Two days later, Sharif announced appointment of Ziauddin as Director General Inter Services Intelligence (DGISI) without consulting Mussharraf. He was now viewed by Mussharraf as Nawaz Sharif’s man and thus kept out of the loop. Some of Ziauddin’s subordinates directly reported to army chief. After Kargil conflict, the gulf between Sharif and Mussharraf widened over a very short period of time. In October 1999, Sharif appointed Ziauddin as army chief when Mussharraf was out of country setting the chain of events that ended in fourth army take over. (For details of 1999 coup see Hamid Hussain. Count Down). Ziauddin was arrested and sacked from the army.
Lieutenant General ® Abdul Qadir Baloch: He is an ethnic Baloch and one of the first Baloch to become lieutenant general. He is an average officer not known for any professional excellence. Once he reached Major General rank, it was probably thought appropriate to promote him one step further for public relations efforts to announce that a Baloch had reached such a high rank. He is a gentleman but has some rough edges and can be a bit difficult in personal relations. He had the confidence of General Mussharraf who sent him as Director General (DG) Rangers of Sindh. After promotion to Lieutenant General rank, he was given the command of Gujranwala based XXX Corps. In the aftermath of September 11, 2001, with angry U.S. bull breathing down their necks forced military leadership to hastily change course. There was some disagreement in the inner circle consisting of Corps Commanders and Principle Staff Officers (PSOs). There was some concern on Mussharraf’s mind in view of a number of senior officers expressing doubts. In October 2001, several senior officers were removed from key positions (Rawalpindi, Lahore, Quetta and Bahawalpur Corps commanders, DGISI and CGS were removed) and in this shuffle Qadir was moved from Gujranwala Corps to Quetta based XII Corps bordering Afghanistan. The manner in which things were moved suggests that all was not well at the top. Qadir was flown in an ISI plane to Quetta to immediately take charge. After retirement, Qadir was appointed governor of Baluchistan province. He developed differences with Mussharraf and resigned. In an interview, Mussharraf passed some derogatory remarks about Qadir and this ticked him off. He had no inclination for politics but after this incident, he contested 2008 elections as independent candidate and despite many hurdles finally entered the parliament. He won his seat in 2013 elections, joined Nawaz Sharif’s faction of Pakistan Muslim League (PML-N) and appointed Minister of State for Tribal and State Affairs.
Lieutenant General ® Abdul Qayyum: He is a gunner officer who served as military secretary to Benazir Bhutto when she was prime Minister. He had an extended tenure with Benazir and served both at Brigadier and Major General rank which is unusual. He was on personal friendly terms with General Pervez Mussharraf who promoted him to lieutenant general rank and appointed him Chairman of Pakistan Ordnance factory (POF). After retirement, he was appointed Chairman of Pakistan Steel Mill. He developed some differences with government on privatization matters and removed from his post. In view of his past association with Benazir, he was probably hoping that if she returned to power, he may get the coveted governorship of Punjab. After Benazir’s assassination, he drifted towards Nawaz Sharif. He is a gentleman but an average officer not known for any professional excellence.
Brigadier ® Javed Iqbal Malik: He was military secretary to Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif at the time of 1999 coup. He sided with newly appointed army Chief Khwaja Ziauddin and he was the only officer who took some action. In fact, Sharif had taken a pip from his shoulders and pinned on Ziauddin’s shoulders making him a four star general. Javed quipped to Ziauddin that ‘Sir; you have been promoted General but I have been demoted to Colonel’. When coup was set in motion by generals loyal to Mussharraf, a small team of soldiers under the command of Major Nisar went to television station and stopped the broadcast of appointment of new army chief. Javed took an armed escort of elite police to television station to check what was going on. Javed had a heated conversation with Major Nisar at television station control room and finally, Javed drew his handgun on Nisar, forcing him to order his men to disarm. The army soldiers were locked in a room and the news of Mussharraf’s removal was re-broadcasted. Later, a larger contingent of soldiers arrived at television station and pulled the plug. After the coup, he was sacked from the army and went in exile to Saudi Arabia with Nawaz Sharif.
|
Posted by admin in ROBOTIC BRAINWASHED TALIBAN on September 28th, 2013
Counterterrorism Center at West Point, US Military Academy
Since the start of the current Taliban insurgency in Afghanistan, U.S.-led NATO forces and the Afghan government have blamed much of the violence on militants based in Pakistan’s tribal areas. Insurgents from groups such as the Haqqani network are able to plan operations from their bases located in Pakistan’s tribal areas, cross the border into Afghanistan, execute attacks, and then retreat back into the relative safety of Pakistan.
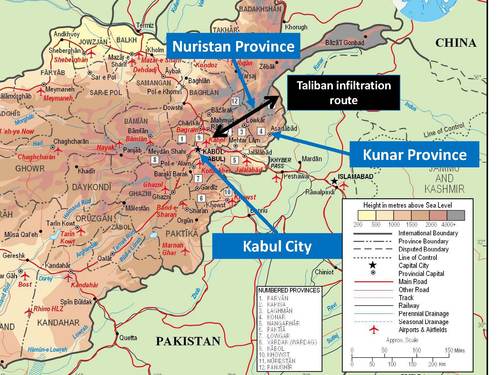 Yet in the last two years, the issue of cross-border attacks has become even more complicated. Pakistan itself is now victim to Pakistani Taliban militants who are sheltering in Afghanistan, crossing the border into Pakistan to conduct attacks, and then retreating back across the Afghan border.[1] Pakistani officials assert that these militants are part of the Pakistani Taliban factions that once pressed for power in the Swat Valley, but were forced to flee into Afghanistan during a successful Pakistani military operation in 2009. Pakistan believes that these militants have regrouped in the border region and are now confident enough to carry out large-scale, cross-border attacks on Pakistani targets.
Yet in the last two years, the issue of cross-border attacks has become even more complicated. Pakistan itself is now victim to Pakistani Taliban militants who are sheltering in Afghanistan, crossing the border into Pakistan to conduct attacks, and then retreating back across the Afghan border.[1] Pakistani officials assert that these militants are part of the Pakistani Taliban factions that once pressed for power in the Swat Valley, but were forced to flee into Afghanistan during a successful Pakistani military operation in 2009. Pakistan believes that these militants have regrouped in the border region and are now confident enough to carry out large-scale, cross-border attacks on Pakistani targets.
Seventeen large-scale, cross-border incursions of militants from Afghanistan to Pakistan have occurred in the last six months.[2] Most of the attacks were carried out in Bajaur Agency of the Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA), an important agency for the Taliban and al-Qa`ida because it shares a border with Kunar Province in Afghanistan—a strategic province from which NATO forces have largely withdrawn.
This article examines the trend of Pakistani Taliban militants using Afghanistan as a staging ground for attacks in Pakistan. It reviews a few key cross-border attacks and speculates whether these operations are part of a larger Taliban strategy.
Cross-Border Attacks
In 2011, security in the border areas remained volatile, with 69 reported clashes and cross-border attacks that killed 225 people.[3] Pakistani military commander Major General Ghulam Qamar asserted that since February 2012, there have been 17 major cross-border incursions where Pakistani Taliban fighters entered Pakistan from Afghanistan to attack Pakistani interests.[4] The incursions have mainly occurred in Bajaur and Mohmand agencies in FATA and Dir and Chitral districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province.
On June 24, 2012, for example, an estimated 100 militants belonging to Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP) entered Pakistan’s Upper Dir District from Afghanistan’s Kunar Province and killed 17 Pakistani soldiers.[5] A few days later, the militants released a video showing the severed heads of the 17 soldiers.[6] The video included a statement from Hakimullah Mehsud, the TTP’s leader, and Maulana Fazlullah, head of the TTP’s Swat chapter.
On July 12, dozens of Pakistani Taliban militants crossed from Afghanistan’s Kunar Province into Pakistan and took scores of villagers hostage, including members of an anti-Taliban militia in the Katkot area of Bajaur Agency.[7] Pakistani forces quickly surrounded the village, killing eight militants.[8]
More recently, Pakistani Taliban militants sheltering in Afghanistan attacked security checkpoints at Inkle Sar and Miskini Darra areas of Samar Bagh Tehsil in Lower Dir District on August 24.[9] The militants were reportedly members of the TTP’s Dir chapter led by Hafizullah.[10]
Also on August 24, hundreds of Pakistani Taliban militants crossed into Pakistan from Kunar Province and attacked security personnel as well as a local tribal militia known as the Salarzai Qaumi lashkar in the Batwar area of Bajaur Agency.[11] Security forces responded, which led to heavy fighting that resulted in the deaths of 30 militants and an estimated six members of the security forces.[12] Fifteen members of the security forces, however, went missing.[13] On August 31, TTP militants released a video showing the severed heads of the 15 soldiers.[14]
Taliban Hideouts in Afghanistan
Pakistani security officials and local tribal elders assert that these cross-border attacks into Pakistani territory have been executed by militants belonging to the Bajaur, Swat and Dir chapters of the TTP, with help from Afghan Taliban militants. Following the Pakistan military’s operations in Swat, Dir and Bajaur in 2009, militants led by Maulana Fazlullah were pushed out of Pakistani territory, and they reportedly fled into Kunar and Nuristan provinces in Afghanistan. From Afghanistan, they prepared for cross-border attacks on Pakistani security forces.[15] With NATO troops largely withdrawing from Kunar and Nuristan throughout 2011, Pakistani analysts suspect that the operating environment has become more conducive to Pakistani Taliban fighters.
The TTP itself has admitted that they use Afghan soil as a springboard to launch attacks on Pakistani security forces—even though the Afghan Taliban deny it.[16] Sirajuddin, a spokesperson for the TTP’s Malakand chapter, said that Maulana Fazlullah is leading militant attacks and remains in contact with Pakistani Taliban fighters based in Pakistan’s Malakand division. Sirajuddin claimed that Fazlullah commands more than 1,000 fighters who move regularly across the porous border between Afghanistan and Pakistan.[17] The exact number of TTP militants in Afghanistan is not known, but Pakistani Major General Athar Abbas said that 200 to 300 militants have been mounting cross-border attacks in Dir, Chitral and Bajaur.[18]
Firm evidence of the TTP’s use of Kunar Province came to light when the head of the TTP’s Bajaur chapter, Mullah Dadullah, was killed in a U.S. airstrike in Shigal district of Kunar Province on August 24, 2012.[19] Dadullah, whose real name was Jamal Said, had a close association with senior members of al-Qa`ida from 2003 to 2007, according to tribal sources. He was the chief of the TTP’s moral police and head of the Taliban’s treasury.[20]
Media reports suggest that Qari Ziaur Rehman, a key al-Qa`ida commander who is from Kunar, as well as Shaykh Dost Muhammad, a Nuristan-based Afghan Taliban leader, are hosting the Pakistani Taliban militants.[21] Rehman is thought to have once been a close confidante of Usama bin Ladin and hosted him temporarily after his escape from the Tora Bora Mountains in 2001.[22] Rehman was sheltered by the Pakistani Taliban in Bajaur Agency for years, and he is now reportedly returning the favor.[23]
Broader Strategic Plan?
Some analysts believe that violence on both sides of the border is a coordinated strategy of al-Qa`ida, the TTP and the Afghan Taliban to damage ties among Islamabad, Kabul and Washington by increasing mutual distrust. Former Afghan Defense Minister Shahnawaz Tanai explained that Taliban elements in both countries helped each other during the fight against the Soviet Union, and this same cooperation extends today.[24] The TTP’s use of so-called “safehavens” in Afghanistan mirrors the Afghan Taliban’s successful use of safehavens in Pakistan.
Other experts argue that the recent rise in cross-border attacks is part of a coordinated strategy to prevent a Pakistani military operation against the Haqqani network.[25] Karachi-based security expert Raees Ahmed believes that the TTP has escalated attacks in Bajaur in response to an impending army operation in North Waziristan, which would coincide with U.S. or Afghan military action against TTP bases in Afghanistan.[26] Militants may be seeking to carve out territory in Bajaur so that they can threaten violence in the settled areas of Malakand division in case Pakistan and the United States coordinate a military offensive.[27]
Conclusion
The recent cross-border incursions on both sides of the border clearly show that Pakistan, Afghanistan and NATO have all failed to clear the strategically important border areas of militants, permitting previously dispersed extremist organizations to regroup and prepare new, large-scale attacks in both countries. Although security forces have begun operations to repel further attacks, they are unlikely to be successful until they deal collectively with the issue of cross-border militancy—a problem to which there are no easy solutions.
Zia Ur Rehman is a journalist and researcher who covers militancy in Pakistan. He has written for The Friday Times, The Jamestown Foundation, Herald and The News International, and contributed to the New York Times.
[1] “Pakistan Accuses Afghanistan of Backing Taliban Enemy,” Reuters, August 5, 2012.
[2] Daily Azadi [Swat], September 7, 2012.
[3] “Pakistan Security Report 2011,” Pakistan Institute for Peace Studies, January 2012.
[4] Daily Azadi [Swat], September 7, 2012.
[5] “Taliban Release Video of Beheaded Pakistani Soldiers,” Agence France-Presse, June 27, 2012.
[6] Ibid.
[7] “Militants Take Villagers Hostage in Bajaur,” Dawn, July 12, 2012.
[8] Ibid.
[9] “Taliban Attack Security Posts in Lower Dir,” Express Tribune, August 24, 2012.
[10] Ibid.
[11] BBC Urdu, August 27, 2012; personal interview, member of Salarzai Qaumi Lashkar, September 3, 2012; “At Least 28 Militants Killed in Bajaur Agency,” Dawn, August 25, 2012.
[12] Ibid.
[13] Anwarullah Khan, “Militants Release Video of Beheaded Soldiers,” Dawn, September 1, 2012.
[14] Ibid.
[15] Personal interviews, elders of Salarzai Qaumi Lashkar, Khar town, Bajaur Agency, Pakistan, March 25, 2012.
[16] Tahir Khan, “Cross-Border Cooperation: Ties That Bind Militants Persist,” Express Tribune, July 8, 2011.
[17] Tahir Khan, “TTP Admits to Having Safe Haven in Afghanistan,” Express Tribune, June 26, 2012.
[18] Zia Khan and Naveed Hussain, “Border Incursions: Suspicions Grow about Afghan Support for TTP,” Express Tribune, September 11, 2011.
[19] Declan Walsh, “Pakistani Militant Leader Dies in Airstrike, NATO Says,” New York Times, August 25, 2012; Javed Hamim Kakar and Khan Wali Salarzai, “Key Haqqani, TTP Leaders Killed in Drone Strikes,” Pajhwok Afghan News, August 25, 2012.
[20] Zia Ur Rehman, “On the Borderline,” Friday Times, September 7-13, 2012.
[21] Khan, “Cross-Border Cooperation: Ties that Bind Militants Persist.”
[22] Khan and Hussain.
[23] Ibid.
[24] Khan, “Cross-Border Cooperation: Ties that Bind Militants Persist.”
[25] “Understanding with US on Joint Action Against Haqqanis,” Dawn, August 6, 2012.
[26] Ibid.
[27] Personal interview, Raees Ahmed, security analyst, Karachi, Pakistan, September 4, 2012.
ARCHIVE ARTICLE: INFILTRATION FROM AFGHANISTAN

At least 200 Taliban fighters crossed from Afghanistan into Pakistan and killed more than 25 soldiers and police, Pakistan’s military says.
The fighters launched an early morning attack on seven military checkpoints in north-west Chitral district.
The military said its troops fought off the attackers, killing 20 of them while the rest fled back into Afghanistan.
It is the latest in a series of cross-border raids that have raised tensions between Pakistan and Afghanistan.
In its statement, the Pakistani military blamed the attack on Pakistan and Afghan Taliban-linked fighters who have sought refuge in the Kunar and Nuristan provinces of Afghanistan, from which the US largely pulled out of a year ago.
It said the “scanty presence” of Nato and Afghan forces in the border areas allow “terrorists” to use those areas as “safe havens”, from which they “have mounted repeated attacks against… security forces posts and isolated villages”.
The military said 25 paramilitary soldiers and police had been killed in Saturday’s attack, but a local officials put the death toll at around 36.